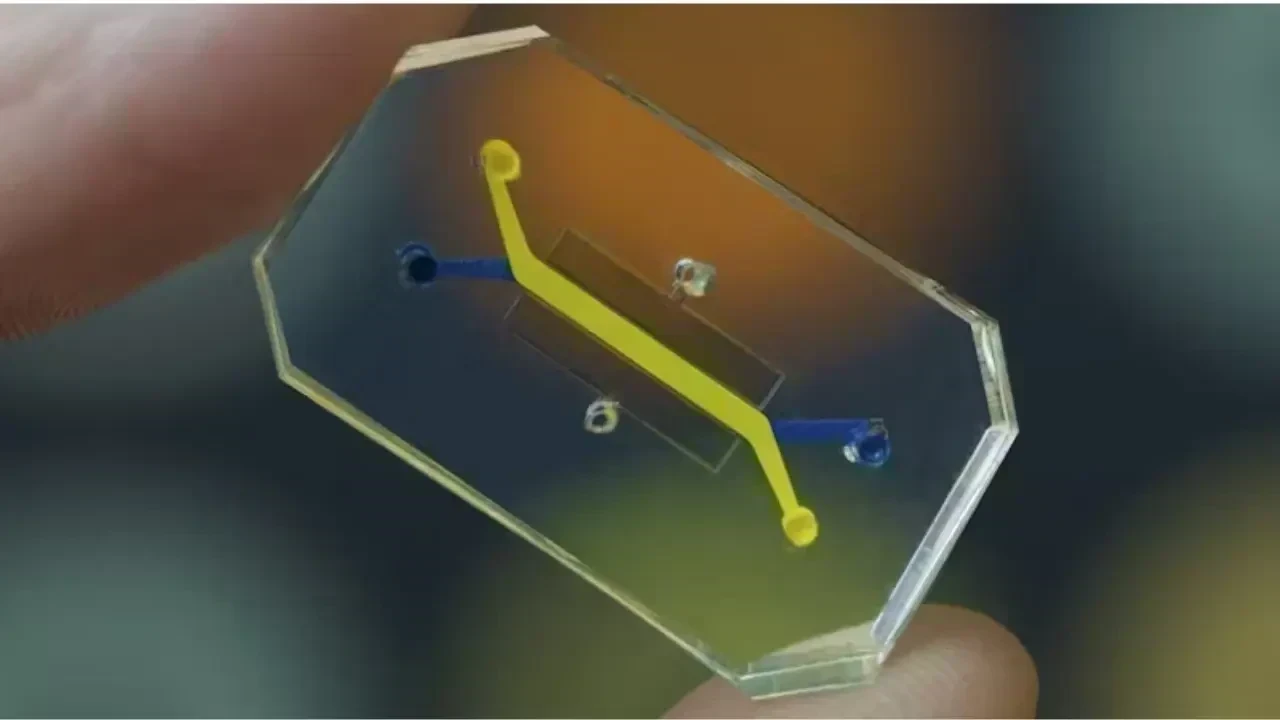
Post by : Anis Karim
The journey of drug discovery is notoriously intricate and costly. On average, developing a medication can span over ten years and rack up billion-dollar expenses, yet the likelihood of failure during human trials remains alarmingly high. Pharmaceutical firms have traditionally depended on animal testing to forecast new drug efficacy and safety. However, physiological discrepancies between animals and humans can lead to unreliable predictions, safety hazards, and squandered investments.
Human Organs-on-Chips—miniaturized biological systems that imitate human organ dynamics—are revolutionizing this landscape. These cutting-edge tools replicate the architecture and functionalities of human tissues, offering an innovative and ethical method for drug testing. They are transitioning from theory to application, being utilized by researchers, biotechnology firms, and even regulatory agencies.
This advancement heralds a new era in drug testing: a scenario where researchers can anticipate human reactions more accurately, lessen reliance on animal studies, and hasten the shift from experimental development to real-world application.
An organ-on-chip is a compact, transparent apparatus—often no bigger than a USB stick—featuring microscopic channels filled with live human cells. These cells are organized in ways that reflect human tissue, allowing the device to replicate organ functions.
Essentially, these chips integrate:
cellular biology
tissue engineering
precise microfluidics
biomechanical principles
Collectively, these factors recreate a human organ's natural setting, factoring in blood circulation, mechanical forces, and chemical influences.
Organs-on-chips can emulate:
the expansion and contraction of lungs
beating heart tissues
intestinal tissues in nutrient uptake
liver cells metabolizing pharmaceuticals
kidney cells filtering waste
This dynamic functionality differentiates them from typical flat cell cultures, enhancing accuracy and predictive value.
The ethical concerns surrounding animal testing are well-documented, and the scientific reliability of such methods is increasingly questioned. Many drugs that are deemed safe in animal studies fail in humans due to fundamental biological differences. In contrast, organs-on-chips leverage actual human cells and imitate human physiological reactions, leading to significantly improved insights into:
toxic effects
drug absorption
metabolic processes
side effects
organ-specific reactions
This advancement could greatly lower clinical trial failure rates while addressing ethical concerns.
Developing a new drug can exceed two billion dollars, with a large portion of the costs stemming from failures during earlier trials. By utilizing organs-on-chips to identify issues sooner, companies can save:
time
money
human lives
resources
The capability of simulating human reactions before going through clinical trials is a remarkable benefit.
Traditional methodologies often fall short when it comes to:
rare diseases
genetic disorders
personalized health issues
Organs-on-chips can be designed using patient-specific cells, facilitating:
tailored medicine
drug assessments customized to an individual’s genetic patterns
modeling of uncommon diseases that are impossible to reproduce in animals
This technology paves the way for therapies that were once deemed too complicated or exorbitant to pursue.
The chip’s channels facilitate fluid movement akin to blood flow in the human body. This continuous flow nourishes the tissues with nutrients and drugs, while simulating mechanical forces to enable realistic organ behavior.
Organs like lungs and intestines are continuously in motion. Organs-on-chips replicate these forces by stretching and compressing tissues in real-time. This feature significantly elevates accuracy in drug reaction forecasts.
The transparency of these chips allows researchers to instantly observe biological responses. This includes:
cell interactions
tissue damage
inflammatory reactions
drug uptake patterns
Such unprecedented visibility isn't achievable through animal models or conventional cultures.
One of the pioneering advancements, the lung-on-chip mimics the rhythmic inflation of lungs. It's utilized to investigate:
respiratory infections
airborne pollutants
asthma
toxicity of drugs on lung tissues
Its reliability has fostered collaborations among research universities, biotech startups, and regulatory bodies.
Cardiac chips replicate the rhythmical beating of heart tissues, allowing scientists to study:
toxicity of heart medications
risks of arrhythmia
metabolic processes
impact of oncological treatments on heart cells
These chips are invaluable since cardiac issues are a leading cause of late-stage drug trial failures.
The liver plays a significant role in drug metabolism. Liver chips aid in identifying:
liver injuries from drugs
metabolic pathways
toxic thresholds
enzyme interactions
This chip is crucial in screening for drugs that could induce liver damage.
The gut is central to digestion, immunity, and the microbiome's roles. These chips assist scientists in researching:
nutrient absorption
gastrointestinal disorders
inflammatory bowel conditions
microbiome responses to drugs
The insights gained here are challenging to achieve with standard laboratory conditions.
The kidneys filter waste and ensure fluid stability. A kidney chip assists researchers in estimating:
nephrotoxic effects
filtration rates
metabolic reactions
Given that kidney issues contribute significantly to drug failure rates, this model is crucial.
Organs-on-chips are enabling researchers to replicate conditions including:
cancer spread
viral outbreaks
chronic inflammatory ailments
genetic diseases
These efforts expedite the development of new treatments and diagnostic modalities.
With increasing global mandates to limit animal testing, cosmetic and chemical manufacturers are shifting to chip-based human models. These platforms enable businesses to safely assess:
skin irritation
chemical safety
allergic reactions
while adhering to ethical research standards.
Regulatory authorities are increasingly recognizing the capabilities of organs-on-chips. These may soon become integral to standardized drug approval processes, reducing dependence on animal testing.
These technologies significantly minimize or eliminate the need for animal testing, aligning with global trends towards ethical research practices.
Utilizing data relevant to human biology results in improved predictions, thereby minimizing clinical trial failures.
Testing processes can be expedited as multiple simulations can be conducted simultaneously.
Each chip can be tailored to specific:
genetic backgrounds
disease profiles
environmental influences
Prior to this, such levels of customization were simply unattainable.
Despite their promise, organs-on-chips come with certain hurdles:
Manufacturing chips in bulk proves to be costly and technologically intricate.
While remarkable, these chips still cannot mirror the full complexity of human organs.
Researchers are still working on multi-organ chips that can simulate complete human body interactions in real-time.
Although promising, most drug approval systems remain heavily reliant on animal data, necessitating substantial reform for chip acceptance.
Scientists are advancing toward developing connected organ systems-on-chips, where multiple chips communicate to replicate human body functions. This development paves the way for:
whole-body drug simulations
understanding multi-organ responses
earlier identification of complications
In time, these integrated systems could provide insights into:
the immune system
metabolic functions
neurological reactions
This innovative approach moves us closer to a reality where drug trials are virtually conducted prior to engaging human subjects.
Human organs-on-chips signify a monumental evolution in biomedical research. By offering human-relevant, ethically sound, and highly accurate testing platforms, this technology holds the potential to reshape drug testing indefinitely.
As society shifts towards personalized medicine, reduced animal testing, and faster therapeutic development, organs-on-chips stand as a pivotal technology that will underpin forthcoming medical advancements. From crafting safer pharmaceuticals to unraveling complex diseases and predicting patientspecific outcomes, this innovation is setting the stage for a more intelligent, humane, and effective future in science.
Disclaimer:
This article serves informational and educational objectives and is not intended as medical or scientific counsel.

Predictheon Wins WHX Xcelerate Innovation Champion 2026
Predictheon won WHX 2026 Xcelerate, earning US$12,000, WHX 2027 space and global exposure for its AI

Omantel Launches Otech to Drive Oman’s Future Tech Vision
Omantel launches Otech to accelerate Oman’s digital transformation, strengthen data sovereignty, exp

Daimler Truck MEA Honors Top Distributors at EliteClass 2025
Daimler Truck MEA hosted EliteClass Awards 2025 in Dubai, honoring top distributors across 19 catego

King Mohammed VI Launches Safran Landing Gear Plant in Morocco
Morocco strengthens its aerospace leadership as King Mohammed VI launches Safran’s €280M landing gea

Qatar Emir Sheikh Tamim Arrives in UAE on Fraternal Visit
Qatar’s Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani arrived in Abu Dhabi on Saturday. UAE President Sheikh

Shaidorov Wins Stunning Olympic Gold as Malinin Falters
Kazakhstan’s Mikhail Shaidorov won men’s figure skating gold after US star Ilia Malinin fell twice.

Shakira’s 5-Show El Salvador Residency Boosts Bukele Image
Shakira’s five sold-out concerts in San Salvador highlight El Salvador’s security shift under Bukele

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin

China Executes 11 Members of Infamous Ming Family Behind Myanmar Scam Operations
China has executed 11 Ming family members, linked to extensive scams and gambling in Myanmar, causin